| Watt Meter |
||
|
The Watt Meter is used to verify the operational integrity of VHF and HF transmission co-ax and antenna systems. It checks forward and reverse power of audio transmissions. The indication result is often referred to as SWR or Standing Wave Ratio.
Aircraft voice communication radios, VHF (118.00MHz – 136.00MHz) and HF (2.0MHz – 29.9999MHz), require the transmission system to dissipate the maximum amount of the transmitted signal. No system is perfect, so there always will be a feedback of some of the signal. If this feedback is within acceptable minimum limits the VHF and HF transceivers will provide proper communication functions. When the co-ax or antenna installation as been compromised, the majority of the transmitted signal will not be radiated from the antenna. This power must go somewhere, so it will travel back down the co-ax to the R/T. The flight crew will report poor or inop transmissions. If the problem is not found and corrected, the result will be numerous R/T replacements and continued pilot write-ups.
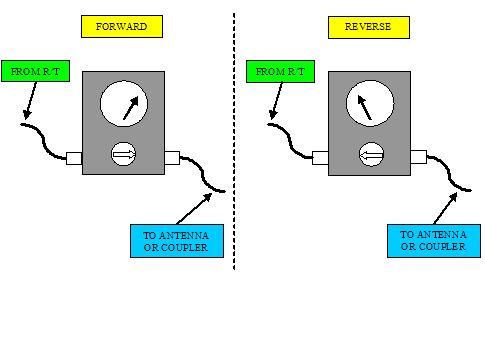
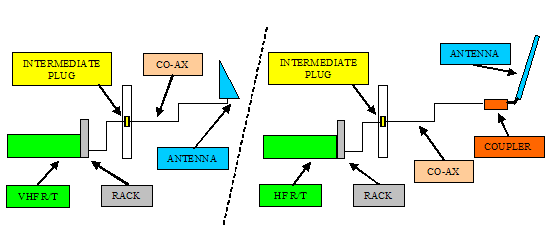
The watt meter is placed "in-line" with the co-ax run. Placing it in the system requires one or two extra co-ax jumpers and a connector adapter kit to match the jumper(s) with the different types of aircraft connectors. It also requires the correct "slug" to be installed in the meter. For VHF, the slug is usually 100MHz – 250MHz with a 25 -50 watt rating. HF slugs are 2MHz – 30MHz with a minimum of 200 watt rating. The arrow on the slug "points" down line towards the antenna for forward power and to the R/T for reverse power. With the affected radio selected and microphone keyed, the forward or reverse power can be measured. Typical aircraft VHF radios output approximately 15 watts. HF radios transmit around 150 watts.
|
 |
|
 |
||
 |
 |
|
|
Helpful Tips for Watt Meter Usage
|
||
 |
||
 |
||
|
THE INFORMATION PRESENTED ON THIS SITE IS TO BE USED AS A GUIDE. APPROVED AIRCRAFT MANUFACTURER MAINTENANCE MANUAL PROCEDURES SHOULD ALWAYS BE FOLLOWED. |
||